Volume 5, Issue 3 (10-2021)
EBHPME 2021, 5(3): 207-218 |
Back to browse issues page
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
khosravizadeh O, Kiaei M Z, Shahsavari S, Mansouran Tazekand N. Factors Influencing Outsourcing Services in Iranian Medical Centers: A Systematic Review. EBHPME 2021; 5 (3) :207-218
URL: http://jebhpme.ssu.ac.ir/article-1-327-en.html
URL: http://jebhpme.ssu.ac.ir/article-1-327-en.html
Student Research Committee, Qazvin University of Medical Sciences, Qazvin, Iran , n.mansoran1367@gmail.com
Full-Text [PDF 2364 kb]
(1186 Downloads)
| Abstract (HTML) (3023 Views)
Full-Text: (465 Views)
Background: Identifying the key factors effective on outsourcing can play a significant role in helping healthcare decision makers to present solutions to improve the outsourcing situation. This study was conducted in order to systematically review the factors influencing the decision making to outsource the services of Iranian medical centers.
Methods: Data was collected through searching for keywords in Google Scholar, PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, Science direct, Magiran, SID and Irandoc databases from January 2010 to December 2020. Also, the quality of the studies was measured and verified by three experts utilizing the Strobe checklist. Researchers classified results achieved by the study.
Results: 10 articles were selected that responded to the study's questions. 44 components in seven dimensions including (economic and financial components, components of laws and regulations (legal), components of supervision and control, components of service type, components of executive capability of the organization, components of the external environment of the organization and components human resources) were recognized on the decision to outsource services in medical centers in Iran.
Conclusion: Policy makers at the decision-making level and managers at the executive level should consider the efficient components and dimensions before deciding to execute outsourcing in units according to the wanted structure, process and consequences, and then make the needed decision regarding the implementation.
Key words: Outsourcing, Ward, Hospital, Medical centers, Iran
Hospitals as one of the most essential levers of health care delivery and the first level of referral are severely affected by global developments (1). The gap between available and required resources is getting wider all around the world. Also, public hospitals, particularly in developing countries, have frequently poor financial performance and attempts to promote performance or apply internal management reforms have not been very effective and satisfactory (2,3). The strategy of providing resources from outside the organization and releasing is one of the methods applied in all areas in recent decades (4). One type of these strategies is outsourcing, which includes outsourcing some activities, factors of production (manpower, equipment, facilities, technologies, and other assets) and allocating the right to decide to outside of the organization under the contract (5). It is possible to use the benefits of private sector management such as attention to efficiency and customer satisfaction applying this strategy. On the other hand, outsourcing enhances the organization's focus on a special activity, making capital funds accessible, accelerating the benefits of restructuring, sharing risk, releasing the resources for other objectives, providing cash into the organization, and reducing and controlling operating costs (6, 7). Studies have also indicated that this strategy can influence access, equity, justice and efficiency in the health system (8). The outsourcing process, like any other process influenced by various factors demands continuous monitoring and evaluation. A study conducted in Kenya indicated that the implementation of outsourcing arrangement by supplier management, contract management, employee competence and legal framework are the key factors affecting the implementation of outsourcing (9). A study conducted in Korea additionally indicated that monitoring strategies are required to improve tangible aspects of service quality for customer satisfaction and reliability among the factors that determine the quality of delivered services (10). Eventually, as stated, increasing patient satisfaction and reducing costs, part of the care has been outsourced in order to achieve more benefits, in recent years in order to increase the quality of health services. However, despite the fact that more than a decade has passed since the implementation of the outsourcing approach in the health sector, there is no comprehensive study of the factors influencing the outsourcing of services so that its results can be applied to examine the capacity of hospital units to establish an outsourcing approach. Hence, regarding the importance of outsourcing and its role in the performance of medical centers, this study was conducted in order to systematically review the studies to recognize the factors influencing the outsourcing services in medical centers in Iran.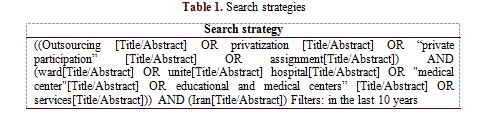 Results
Results
65 studies were recognized through a search of the database, that 10 cases were rejected due to repetition. After screening, the titles and abstracts of 25 other studies were removed; 20 articles were then removed from the study process by full-text screening, and 10 articles were eventually selected that responded to the questions of this study (Figure 1). The reviewed studies have been summarized in the form of author / year of publication, place of study, study title, study population and type of study, study method and key results according to Table 2.
Factors affecting outsourcing
44 factors affecting the decision to outsource services were recognized by examining the
above 10 studies. These factors were finally conceptualized in the form of 7 dimensions by summarizing the opinions (Table 3).
2) Rules and regulations dimension
The components of this dimension imply the observance of legal items from inquiring the contractor and concluding the contract to observe the supervisory laws. According to the study, most studies have considered important to complete the outsourcing process within a legal framework. Adherence to and applying the
law in this field also guarantees the performance of outsourced service and its appropriate implementation and protects the interests of the parties to the contract.
3) Monitoring and control dimension
The components of this dimension, which ensure the progress of outsourced services with agreed and predetermined quantity and quality require to design a comprehensive monitoring system from the beginning to the end of the contract. According to studies in this field, determining the clear and measurable standards and also documenting the results of successive controls affect significantly the outsourcing success.
4) Type of service dimension
One of the most essential factors affecting the outsourcing is the specific characteristics of the type of service. Studies indicate that outsourcing of some types of services is not needed and does not have any benefit to the organization, while in some cases, it has produced losses.
5) Executive capacity of the organization dimension
The components of this dimension mean the capacity of the organization to implement the pillars of outsourcing. Studies conducted in this field have indicated that the participation and cooperation of different components of the organization, for example, financial support and manpower support in order to outsource a service that guarantees a successful outsourcing.
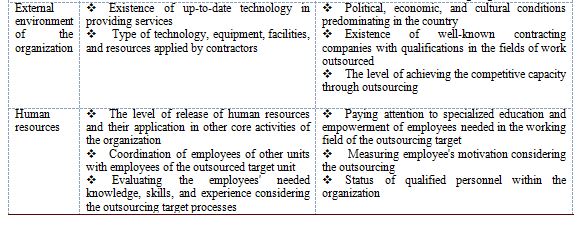
6) External environment of the organization dimension
The components of this dimension clarify that the organization as an open system in each of its activities depends on conditions outside the organization. The results of the study explained that outsourcing depends on the existence of a competent foreign supplier as well as the legal, economic, cultural and political support platform.
7) Human resources dimension
Components of this dimension refer to the most essential source of any organization that directly influences the efficiency and quality of service. Studies have explained that outsourcing is specifically affected by the capacity and abilities of the manpower responsible for the service and the type of relationship of internal forces with the staff related to the outsourcing unit.
According to the recognition and importance of the above dimensions and factors, Table 4 presents the recommendations achieved by the review to obtain a successful outsourcing..JPG)

.JPG)
.JPG)
.JPG)
Discussion
A systematic analysis of studies in the field of outsourcing was conducted and the research team then conceptualized them to analyze the studies and extract the factors and components influencing the outsourcing of services in medical centers in the form of 7 economic and financial dimensions, laws, and regulations. (Legal), supervision and control, type of service, the executive capability of the organization, external environment of the organization, and human resources. Operational suggestions to improve effective outsourcing decision-making were also summarized and presented.
As the results show, economic and financial factors affect significantly outsourcing, which is also confirmed by the studies conducted by Modiri and Ansari Farshad (23), Alam Tabriz and Shayesteh (24). Also, a study conducted on the outsourcing of information technology services in Italy in agreement with this study showed the role of financial resources of the organization and economic factors in outsourcing (25). It is possible to state in explaining the findings that costs can be shared among more companies due to the scale savings in outsourcing and consequently, costs can be reduced. Also, when a service provider demands more money for service, the organization makes a more informed decision by comparing free internal services.
According to the findings, the factors of rules and regulations on outsourcing were recognized. In this field, the results of research conducted by Asousheh et al. (26) are in agreement with this finding. A review of business outsourcing models has also recognized adherence to rules and regulations as guaranteeing the sustainability of outsourcing (27). In this respect, it should be stated that the contractual (legal) agreement between the public and private sectors at a specific time, within the framework of negotiations, is determined by the amount of risk and the set rewards are executed, and each of these sectors achieves notable benefits.
According to the findings, the components of monitoring and control in this study and also many types of research, including; the study conducted by Mosazadeh et al. (28) affect significantly outsourcing. In this regard, a study conducted in Malaysia has highlighted the importance of estimating and selecting suppliers, which is considered a control task (29). In fact, observing the general principles of contracts drives cost savings in transactions (such as the cost of negotiating and contracting, selecting and evaluating a supplier) and achieving competitive competence, that it depends on the continuous monitoring and control of the outsourcing process by health care organizations (the transferring organization).
According to the findings, the type of service component in agreement with the study conducted by Mosazadeh et al. (28) is effective on outsourcing. In this respect, Alam Tabriz and Shayesteh (24) have declared that conducting the processes of the organization demands resources, expertise, and attention, which is frequently not provided at enough level for the organization and must be provided from external sources to focus on core competencies. And stay in the competition cycle.
In this present study, which is also consistent with the study conducted by Modiri and Ansari (23), the executive capability factor of the organization was identified as having a key influence on outsourcing. It should be stated that rapid changes in business have forced senior executives to apply outsourcing strategies to focus on current successes and investments to increase the competitive advantage. In fact, many executives considered outsourcing as the only way to sustain a competitive business position (30).
According to the findings, the components of the external environment of the organization were effective on outsourcing according to the study conducted by Alam Tabriz and Shayesteh (24). This component focuses on service providers and effective legal factors. Regardless of the number of suppliers, the greater the assessed ability of potential suppliers to perform an activity, the greater the tendency to outsource. Furthermore, according to the findings; Sarbo's (27) review of outsourcing models have also recognized that conditions outside the organization, including political, economic, and cultural affect the sustainability of outsourcing.
In this study, factors related to human resources are immediately in agreement with the research conducted by Farhoudi et al. (31) and Navidi et al. (32) on outsourcing. A study conducted in Spain also confirms the results of this study by introducing a sense of justice in domestic employees by strengthening the participation of domestic employees with outsourced employees (33). Additionally, a study conducted in Poland in the field of financial services outsourcing has highlighted the importance of human resource capacity and skills used in outsourcing inconsistent with these results (34). Ultimately, it should be stated that this study is one of the first systematic reviews of the factors influencing the outsourcing of services in medical centers in Iran. On the other hand, the restriction of the study is that it cannot declare to have completely reported all the dimensions and components that affect outsourcing decisions from other fields and sectors.
Conclusion
Outsourcing in organizations should be considered especially as a platform for improving the economic situation, improving efficiency, achieving higher productivity, and also the objectives of a resistive economy. The results of this review indicated that economic and financial dimensions, rules and regulations, supervision and control, type of service, the executive capability of the organization, external environment of the organization, and human resources are effective in outsourcing of medical centers that policymakers and decision-makers should discuss these dimensions and components from outsourcing to take proper action and achieve the expected
results.
Officials and decision-makers must make proper decisions considering the management of outsourced units, quantitative and qualitative evaluation of these units in order to maintain or transfer these units in addition to monitoring and controlling and paying attention to the observance of legal components. Specialized education and empowerment of employees, classification of qualified personnel, and attention to employee motivation should be on the agenda of the managers of these units in order to sustain the outsourced units of medical centers and improve the quality and success of these units in addition to paying attention to providing services based on a specific procedure. Also, since the evaluation of outsourced units is directly affected by the executive capability of the organization, senior managers should focus on internal capacities and capabilities, internal support for outsourcing, flexibility, and organizational participation and factors outside the organization.
Conflict of interests
The authors declared no conflict of interests.
Authors' contributions
Khosravizadeh O designed research; Kiaei MZ and Mansouran tazekand N conducted research; Shahsavari S analyzed data; and Shahsavari S and Mansouran tazekand N wrote manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
Not applicable.
Methods: Data was collected through searching for keywords in Google Scholar, PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, Science direct, Magiran, SID and Irandoc databases from January 2010 to December 2020. Also, the quality of the studies was measured and verified by three experts utilizing the Strobe checklist. Researchers classified results achieved by the study.
Results: 10 articles were selected that responded to the study's questions. 44 components in seven dimensions including (economic and financial components, components of laws and regulations (legal), components of supervision and control, components of service type, components of executive capability of the organization, components of the external environment of the organization and components human resources) were recognized on the decision to outsource services in medical centers in Iran.
Conclusion: Policy makers at the decision-making level and managers at the executive level should consider the efficient components and dimensions before deciding to execute outsourcing in units according to the wanted structure, process and consequences, and then make the needed decision regarding the implementation.
Key words: Outsourcing, Ward, Hospital, Medical centers, Iran
Introduction
Hospitals as one of the most essential levers of health care delivery and the first level of referral are severely affected by global developments (1). The gap between available and required resources is getting wider all around the world. Also, public hospitals, particularly in developing countries, have frequently poor financial performance and attempts to promote performance or apply internal management reforms have not been very effective and satisfactory (2,3). The strategy of providing resources from outside the organization and releasing is one of the methods applied in all areas in recent decades (4). One type of these strategies is outsourcing, which includes outsourcing some activities, factors of production (manpower, equipment, facilities, technologies, and other assets) and allocating the right to decide to outside of the organization under the contract (5). It is possible to use the benefits of private sector management such as attention to efficiency and customer satisfaction applying this strategy. On the other hand, outsourcing enhances the organization's focus on a special activity, making capital funds accessible, accelerating the benefits of restructuring, sharing risk, releasing the resources for other objectives, providing cash into the organization, and reducing and controlling operating costs (6, 7). Studies have also indicated that this strategy can influence access, equity, justice and efficiency in the health system (8). The outsourcing process, like any other process influenced by various factors demands continuous monitoring and evaluation. A study conducted in Kenya indicated that the implementation of outsourcing arrangement by supplier management, contract management, employee competence and legal framework are the key factors affecting the implementation of outsourcing (9). A study conducted in Korea additionally indicated that monitoring strategies are required to improve tangible aspects of service quality for customer satisfaction and reliability among the factors that determine the quality of delivered services (10). Eventually, as stated, increasing patient satisfaction and reducing costs, part of the care has been outsourced in order to achieve more benefits, in recent years in order to increase the quality of health services. However, despite the fact that more than a decade has passed since the implementation of the outsourcing approach in the health sector, there is no comprehensive study of the factors influencing the outsourcing of services so that its results can be applied to examine the capacity of hospital units to establish an outsourcing approach. Hence, regarding the importance of outsourcing and its role in the performance of medical centers, this study was conducted in order to systematically review the studies to recognize the factors influencing the outsourcing services in medical centers in Iran.
Materials and Methods
Type of study
This study is a systematic review study that has been conducted to identify the factors influencing the successful implementation of outsourcing of medical services in Iran in 2020. Also, this study is in full agreement with the preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analysis (PRISMA) (11).
Questions and research framework
This study has been conducted to respond to two questions: "What are the factors influencing the successful implementation of outsourcing?" and "What are the operational strategies for effective outsourcing decision making?"
Search strategy
Data have been collected by searching the Google Scholar, PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, Science direct, Magiran, SID and Irandoc databases from January 2010 to December 2020. Some reliable key journals were additionally manually searched to identify and cover more articles. Keywords include "outsourcing", "privatization", "private participation", "assignment", "ward", "unite", "hospital", "medical center", "educational and medical centers", "services", "outsourcing", "ward", "unit", "hospital", "medical center" and "Iran", "privatization", "private sector participation", "services" and privatization. AND, OR, and NOT were used to combine or restrict search results, and the search protocol was limited to the last 10 years (Table 1).
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Inclusion criteria to select articles related to the field of research include: 1- Studies that have been conducted in the field of outsourcing of medical centers in the last ten years 2- All descriptive, analytical and cross-sectional studies with different methodologies 3- The studies were only in Persian and English. Exclusion criteria also include: 1- Studies that have been conducted in other service fields 2- Studies that cannot be accessed.
Screening and selection of studies
Articles were selected with the keywords mentioned in the titles and their abstracts, repetitive articles were then recognized and removed from the review process. In the next steps, the abstract and then the full text of the articles were examined and studies that included exclusion criteria and had a weak relationship with the purposes of the study were identified and removed. A list of the titles of all the articles searched in the database was eventually provided. Screening studies and irrelevant articles were removed to determine the most proper list. Selected articles were finally included in the study. The selected articles were fully studied and examined. Titles were evaluated and organized and repetitive records were found and removed using Resource Management Software (EndNote X8).
Quality assessment and data extraction
The achieved articles were evaluated by three researchers applying the STROBE checklist after the search and accordingly, the high-quality articles were determined. This checklist is one of the best instruments applied to verify the quality of observational articles. This checklist measures 22 items in the sections of Title, Introduction, Method, Results, and Discussion and Conclusion (12). Articles that did not have more than 50 % checklist items; were removed and data were extracted after quality evaluation. The needed data were extracted and summarized in the form of author / year of publication, place of study, study title, study population and type of study, study method and key results.
Categorizing the results
The data extracted in this study were conceptualized in the form of dimensions, components and executive suggestions. Three researchers individually conceptualized the components extracted from the studies in different dimensions in the process of this analysis; the provided dimensions and components were then compared, and the researchers assembled and presented a single agreed grouping.
This study was the result of a part of the master's thesis of the Faculty of Health, which has been conducted by obtaining the needed licenses from Qazvin University of Medical Sciences. (Code of ethics: IR.QUMS.REC.1397.210)
Type of study
This study is a systematic review study that has been conducted to identify the factors influencing the successful implementation of outsourcing of medical services in Iran in 2020. Also, this study is in full agreement with the preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analysis (PRISMA) (11).
Questions and research framework
This study has been conducted to respond to two questions: "What are the factors influencing the successful implementation of outsourcing?" and "What are the operational strategies for effective outsourcing decision making?"
Search strategy
Data have been collected by searching the Google Scholar, PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, Science direct, Magiran, SID and Irandoc databases from January 2010 to December 2020. Some reliable key journals were additionally manually searched to identify and cover more articles. Keywords include "outsourcing", "privatization", "private participation", "assignment", "ward", "unite", "hospital", "medical center", "educational and medical centers", "services", "outsourcing", "ward", "unit", "hospital", "medical center" and "Iran", "privatization", "private sector participation", "services" and privatization. AND, OR, and NOT were used to combine or restrict search results, and the search protocol was limited to the last 10 years (Table 1).
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Inclusion criteria to select articles related to the field of research include: 1- Studies that have been conducted in the field of outsourcing of medical centers in the last ten years 2- All descriptive, analytical and cross-sectional studies with different methodologies 3- The studies were only in Persian and English. Exclusion criteria also include: 1- Studies that have been conducted in other service fields 2- Studies that cannot be accessed.
Screening and selection of studies
Articles were selected with the keywords mentioned in the titles and their abstracts, repetitive articles were then recognized and removed from the review process. In the next steps, the abstract and then the full text of the articles were examined and studies that included exclusion criteria and had a weak relationship with the purposes of the study were identified and removed. A list of the titles of all the articles searched in the database was eventually provided. Screening studies and irrelevant articles were removed to determine the most proper list. Selected articles were finally included in the study. The selected articles were fully studied and examined. Titles were evaluated and organized and repetitive records were found and removed using Resource Management Software (EndNote X8).
Quality assessment and data extraction
The achieved articles were evaluated by three researchers applying the STROBE checklist after the search and accordingly, the high-quality articles were determined. This checklist is one of the best instruments applied to verify the quality of observational articles. This checklist measures 22 items in the sections of Title, Introduction, Method, Results, and Discussion and Conclusion (12). Articles that did not have more than 50 % checklist items; were removed and data were extracted after quality evaluation. The needed data were extracted and summarized in the form of author / year of publication, place of study, study title, study population and type of study, study method and key results.
Categorizing the results
The data extracted in this study were conceptualized in the form of dimensions, components and executive suggestions. Three researchers individually conceptualized the components extracted from the studies in different dimensions in the process of this analysis; the provided dimensions and components were then compared, and the researchers assembled and presented a single agreed grouping.
This study was the result of a part of the master's thesis of the Faculty of Health, which has been conducted by obtaining the needed licenses from Qazvin University of Medical Sciences. (Code of ethics: IR.QUMS.REC.1397.210)
 Results
Results65 studies were recognized through a search of the database, that 10 cases were rejected due to repetition. After screening, the titles and abstracts of 25 other studies were removed; 20 articles were then removed from the study process by full-text screening, and 10 articles were eventually selected that responded to the questions of this study (Figure 1). The reviewed studies have been summarized in the form of author / year of publication, place of study, study title, study population and type of study, study method and key results according to Table 2.
Factors affecting outsourcing
44 factors affecting the decision to outsource services were recognized by examining the
above 10 studies. These factors were finally conceptualized in the form of 7 dimensions by summarizing the opinions (Table 3).
- Economic and financial dimension
2) Rules and regulations dimension
The components of this dimension imply the observance of legal items from inquiring the contractor and concluding the contract to observe the supervisory laws. According to the study, most studies have considered important to complete the outsourcing process within a legal framework. Adherence to and applying the
law in this field also guarantees the performance of outsourced service and its appropriate implementation and protects the interests of the parties to the contract.
3) Monitoring and control dimension
The components of this dimension, which ensure the progress of outsourced services with agreed and predetermined quantity and quality require to design a comprehensive monitoring system from the beginning to the end of the contract. According to studies in this field, determining the clear and measurable standards and also documenting the results of successive controls affect significantly the outsourcing success.
4) Type of service dimension
One of the most essential factors affecting the outsourcing is the specific characteristics of the type of service. Studies indicate that outsourcing of some types of services is not needed and does not have any benefit to the organization, while in some cases, it has produced losses.
5) Executive capacity of the organization dimension
The components of this dimension mean the capacity of the organization to implement the pillars of outsourcing. Studies conducted in this field have indicated that the participation and cooperation of different components of the organization, for example, financial support and manpower support in order to outsource a service that guarantees a successful outsourcing.
6) External environment of the organization dimension
The components of this dimension clarify that the organization as an open system in each of its activities depends on conditions outside the organization. The results of the study explained that outsourcing depends on the existence of a competent foreign supplier as well as the legal, economic, cultural and political support platform.
7) Human resources dimension
Components of this dimension refer to the most essential source of any organization that directly influences the efficiency and quality of service. Studies have explained that outsourcing is specifically affected by the capacity and abilities of the manpower responsible for the service and the type of relationship of internal forces with the staff related to the outsourcing unit.
According to the recognition and importance of the above dimensions and factors, Table 4 presents the recommendations achieved by the review to obtain a successful outsourcing.
.JPG)

.JPG)

.JPG)
.JPG)
Discussion
A systematic analysis of studies in the field of outsourcing was conducted and the research team then conceptualized them to analyze the studies and extract the factors and components influencing the outsourcing of services in medical centers in the form of 7 economic and financial dimensions, laws, and regulations. (Legal), supervision and control, type of service, the executive capability of the organization, external environment of the organization, and human resources. Operational suggestions to improve effective outsourcing decision-making were also summarized and presented.
As the results show, economic and financial factors affect significantly outsourcing, which is also confirmed by the studies conducted by Modiri and Ansari Farshad (23), Alam Tabriz and Shayesteh (24). Also, a study conducted on the outsourcing of information technology services in Italy in agreement with this study showed the role of financial resources of the organization and economic factors in outsourcing (25). It is possible to state in explaining the findings that costs can be shared among more companies due to the scale savings in outsourcing and consequently, costs can be reduced. Also, when a service provider demands more money for service, the organization makes a more informed decision by comparing free internal services.
According to the findings, the factors of rules and regulations on outsourcing were recognized. In this field, the results of research conducted by Asousheh et al. (26) are in agreement with this finding. A review of business outsourcing models has also recognized adherence to rules and regulations as guaranteeing the sustainability of outsourcing (27). In this respect, it should be stated that the contractual (legal) agreement between the public and private sectors at a specific time, within the framework of negotiations, is determined by the amount of risk and the set rewards are executed, and each of these sectors achieves notable benefits.
According to the findings, the components of monitoring and control in this study and also many types of research, including; the study conducted by Mosazadeh et al. (28) affect significantly outsourcing. In this regard, a study conducted in Malaysia has highlighted the importance of estimating and selecting suppliers, which is considered a control task (29). In fact, observing the general principles of contracts drives cost savings in transactions (such as the cost of negotiating and contracting, selecting and evaluating a supplier) and achieving competitive competence, that it depends on the continuous monitoring and control of the outsourcing process by health care organizations (the transferring organization).
According to the findings, the type of service component in agreement with the study conducted by Mosazadeh et al. (28) is effective on outsourcing. In this respect, Alam Tabriz and Shayesteh (24) have declared that conducting the processes of the organization demands resources, expertise, and attention, which is frequently not provided at enough level for the organization and must be provided from external sources to focus on core competencies. And stay in the competition cycle.
In this present study, which is also consistent with the study conducted by Modiri and Ansari (23), the executive capability factor of the organization was identified as having a key influence on outsourcing. It should be stated that rapid changes in business have forced senior executives to apply outsourcing strategies to focus on current successes and investments to increase the competitive advantage. In fact, many executives considered outsourcing as the only way to sustain a competitive business position (30).
According to the findings, the components of the external environment of the organization were effective on outsourcing according to the study conducted by Alam Tabriz and Shayesteh (24). This component focuses on service providers and effective legal factors. Regardless of the number of suppliers, the greater the assessed ability of potential suppliers to perform an activity, the greater the tendency to outsource. Furthermore, according to the findings; Sarbo's (27) review of outsourcing models have also recognized that conditions outside the organization, including political, economic, and cultural affect the sustainability of outsourcing.
In this study, factors related to human resources are immediately in agreement with the research conducted by Farhoudi et al. (31) and Navidi et al. (32) on outsourcing. A study conducted in Spain also confirms the results of this study by introducing a sense of justice in domestic employees by strengthening the participation of domestic employees with outsourced employees (33). Additionally, a study conducted in Poland in the field of financial services outsourcing has highlighted the importance of human resource capacity and skills used in outsourcing inconsistent with these results (34). Ultimately, it should be stated that this study is one of the first systematic reviews of the factors influencing the outsourcing of services in medical centers in Iran. On the other hand, the restriction of the study is that it cannot declare to have completely reported all the dimensions and components that affect outsourcing decisions from other fields and sectors.
Conclusion
Outsourcing in organizations should be considered especially as a platform for improving the economic situation, improving efficiency, achieving higher productivity, and also the objectives of a resistive economy. The results of this review indicated that economic and financial dimensions, rules and regulations, supervision and control, type of service, the executive capability of the organization, external environment of the organization, and human resources are effective in outsourcing of medical centers that policymakers and decision-makers should discuss these dimensions and components from outsourcing to take proper action and achieve the expected
results.
Officials and decision-makers must make proper decisions considering the management of outsourced units, quantitative and qualitative evaluation of these units in order to maintain or transfer these units in addition to monitoring and controlling and paying attention to the observance of legal components. Specialized education and empowerment of employees, classification of qualified personnel, and attention to employee motivation should be on the agenda of the managers of these units in order to sustain the outsourced units of medical centers and improve the quality and success of these units in addition to paying attention to providing services based on a specific procedure. Also, since the evaluation of outsourced units is directly affected by the executive capability of the organization, senior managers should focus on internal capacities and capabilities, internal support for outsourcing, flexibility, and organizational participation and factors outside the organization.
Conflict of interests
The authors declared no conflict of interests.
Authors' contributions
Khosravizadeh O designed research; Kiaei MZ and Mansouran tazekand N conducted research; Shahsavari S analyzed data; and Shahsavari S and Mansouran tazekand N wrote manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
Not applicable.
Type of Study: Review Article |
Subject:
Healt care Management
Received: 2021/01/4 | Accepted: 2021/10/4 | Published: 2021/10/4
Received: 2021/01/4 | Accepted: 2021/10/4 | Published: 2021/10/4
References
1. 1. Jabbari Beyrami H, Bakhshiyan F. Decentralization in health systems. Tabriz: Research Deputy of Tabriz University of Medical Sciences. Medical Journal Of Tabriz University Of Medical Sciences. 2007.
2. Gholamzadehnikjo R. Designing a model of public-private partnership in governmental hospitals. Tabriz University of Medical Sciences. 2012.
3. Barati O, Dehghan H, Yusefi A, Najibi M. A study of the status before and after outsourced pharmacies of Shiraz University of Medical Sciences in 2014: A short report. Journal of Rafsanjan University of Medical Sciences. 2017; 16(7): 691-700.
4. Zhirafar M, Vatankhah S, Seyedein SH. Relationship between contract management and staff satisfaction in hospitals affiliated To Tehran University Of Medical Sciences. Payavard Salamat. 2013; 6(4): 311-8. [In Persian]
5. Khodaverdi R, Zohre E. Outsourcing strategy; benefits, problems and challenges. Expertise Journal of Parks and Growing Center. 2010: 65-72.
6. Arastoozadeh F, Torabipour A. Comparison of services' quality in outsourced and non-outsourced clinical laboratory in Ahvaz University Hospitals, 2016. Journal of Healthcare Management. 2017; 8(2): 87-97. [In Persian]
7. Loevinsohn B, April H. Buying resultsu Contracting for health service delivery in developing countries. The Lancet. 2005; 366(9486): 676-81. [DOI:10.1016/S0140-6736(05)67140-1]
8. Nazari K, Ahmadzadeh M, Ghanbari M. Outsourcing and model presentation in Khorasan Razavi Water and Sewerage Company, 2015. Tehran International Conference on Water and Wastewater.
9. Moris F. Intangibles trade and MNEs: Supply-chain trade in R&D services and innovative subsidiaries. Journal of Industry, Competition and Trade. 2018; 18(3): 349-71. [DOI:10.1007/s10842-017-0265-0]
10. Kim SS. Difference in recognition of internal customer service quality of outsourcing staff in hospital using IPA. Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics. 2018; 43(1): 80-8. [DOI:10.21032/jhis.2018.43.1.80]
11. Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gøtzsche PC, Ioannidis JPA, et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: Explanation and elaboration. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology. 2009; 62(10): 1-34. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000100. [DOI:10.1371/journal.pmed.1000100]
12. Von Elm E, Altman DG. The strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. Annals of Internal Medicine. 2007; 147(8): 573-7. [DOI:10.7326/0003-4819-147-8-200710160-00010]
13. Khosravizadeh O, Shahsavari S, Baghian N, Maleki A, Hossienpour F, Jozyari B. Do medical records outsourcing affect insurance deductions? An interrupted time series in Qazvin's trauma center. Journal of Surgery and Trauma. 2019; 7(4): 152-60. [DOI:10.32592/Jsurgery.2019.7.4.105]
14. Taghipourian M, Alizade B. The role of corporate culture on the quality of working relationships during outsourcing activities in Tehran University of Medical Sciences. Journal of Hospital. 2018; 17(1): 109-19.
15. Jannati A, Jabbari Beirami H, Mousazadeh Y. Designing a downsizing model for hospitals of Tabriz University of Medical Sciences. Journal of Health. 2017; 8(3): 336-49.
16. Jahangiri A. Ranking different regions of Iran in terms of the level of health services outsourcing and indirect care activities of the social security organization via using multiple attribute decision making method in year 2016. Health Information Management. 2018: 34-9.
17. Parsamin S, O NP. The effect of outsourcing on satisfaction and observance of the rights of patients referring to the radiology departments of selected hospitals in Tehran. Healthcare Management. 2015; 6(1): 51-8.
18. Joudaki H, Heidari M, Geraili B. Outsourcing of hospitals services : Lessons learned from the experience. Journal of Health Based Research. 2015; 1(1): 13-23.
19. Barati O, Dehghan H, Yusefi A, Najibi M. A study of the status before and after outsourced pharmacies of Shiraz University of Medical Sciences in 2014: A short report. Journal of Rafsanjan University of Medical Sciences. 2017; 16(7): 691-700. [In Persian]
20. Ferdosi M, Farahabadi S, Mofid M, Rejalian F, Haghighat M, Naghdi P. Evaluating the outsourcing of nursing services in Kashani hospital, Isfahan. Health Inform Manage. 2012; 9(7): 989-96.
21. Ghanbari AM, Ahmadzadeh M. The effect of out-sourcing on health services costs of Qom Health Center by activity based costing approach. Journal of Accounting and Auditing Researches. 2017; 9(33): 88-107.
22. Arab M, Hamidi M, Ghiasvand H, Akbarisari A, Moghari J, Dorodi R. Determining the cost of radiology services in selected hospitals affiliated to Tehran University of Medical Sciences using activity-based costing method in 2010. Hospital Journal. 2010; 11(3): 27-36.
23. Modiri M, Ansarifarshad A. Improving a class decision-making model in the business outsourcing (IT) process using the MCDM approach. Quarterly Journal of Development and Transformation Management. 2013; 10.
24. Alamtabriz A, Shayesteh R. Evaluation and prioritization of outsourcing of provincial tax work processes in the Tax Affairs Organization with fuzzy TOPSIS approach. Tax Research Journal. 2011; 10(58).
25. Popoli P. Conceptualizing relational resources as critical factor for IT outsourcing success. International Journal of Business and Management. 2017; 12. [DOI:10.5539/ijbm.v12n10p43]
26. Asoshe A, Divandari A, Karami A, Yazdani H. Identifying critical success factors in information systems outsourcing risk management in Iranian commercial banks. Journal of Information Technology Management. 2001; 1(3): 18-3.
27. Sarba A, Mateescu R, Buchmuller M. Governance as a key factor for ensuring the sustainability of outsourcing models. The 4th International Conference on Management, Leadership and Govrnance. 2016; (4): 466-74.
28. Mousazadeh Y, Jabaribeirami H, Janati A, AsghariJafarabadi M. Identifying and prioritizing hospital's units for outsourcing based on related indicators: A qualitative study. Journal of Health. 2013; 4(2): 122-33. [In Persian]
29. Hiean T, Samah I, Abashah A. Factor of vendor selection and employees' morale towards human resource outsourcing decision in organization. MATEC Web of Conferences. 2018; 150. [DOI:10.1051/matecconf/201815005019]
30. Bolat T, Yılmaz Q. The relationship between outsourcing and organizational performance. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management. 2009. [DOI:10.1108/09596110910930151]
31. Farhodi H, Abdi B, Aghamohammadi V. Identifying and prioritizing the critical factors for the success of information systems in the National Iranian Petroleum Products Distribution Company with a strategic planning approach. New Process. 2015; 52.
32. Navidi A, Taghipour ZA, Ahmadi SAA. Presenting the educational and research activities outsourcing model in organizations governmental (case study: Great Tehran Electrical Distribution Company). Managing Education in Organization. 2017: 179-210.
33. Zoghbi-Manrique-de-Lara P, Ting-Ding J. Employees' justice perceptions as a factor influencing successful outsourcing in the hospitality industry. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management. 2017; 29(6): 1619-37. [DOI:10.1108/IJCHM-09-2015-0477]
34. Bagianska A. Professional knowledge and skills as a key factor in the development of the outsourcing of financial and accounting services in Poland. Journal of Studia i Materiały. 2016; (20): 52-64. [DOI:10.7172/1733-9758.2016.20.4]
Send email to the article author
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |







